n8n HTTP Request Node Documentation: Beginner to Advanced Guide
Introduction to n8n HTTP Request Node Documentation
The HTTP Request Node in n8n is one of its most powerful features—it lets you connect with any API on the internet, even if no dedicated integration exists.
Whether you’re calling the OpenAI API, fetching data from Google Maps, or posting form data to your own backend, the HTTP Request Node is your universal connector.
This guide explains the official documentation in plain language, complete with examples, screenshots, and best practices.
What is the HTTP Request Node in n8n?
The HTTP Request Node allows you to:
- Send GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE requests.
- Work with JSON, Form, or XML bodies.
- Authenticate with APIs using headers or OAuth2.
- Pass query parameters dynamically from other nodes.
It’s like Postman, but built into your automation workflows.
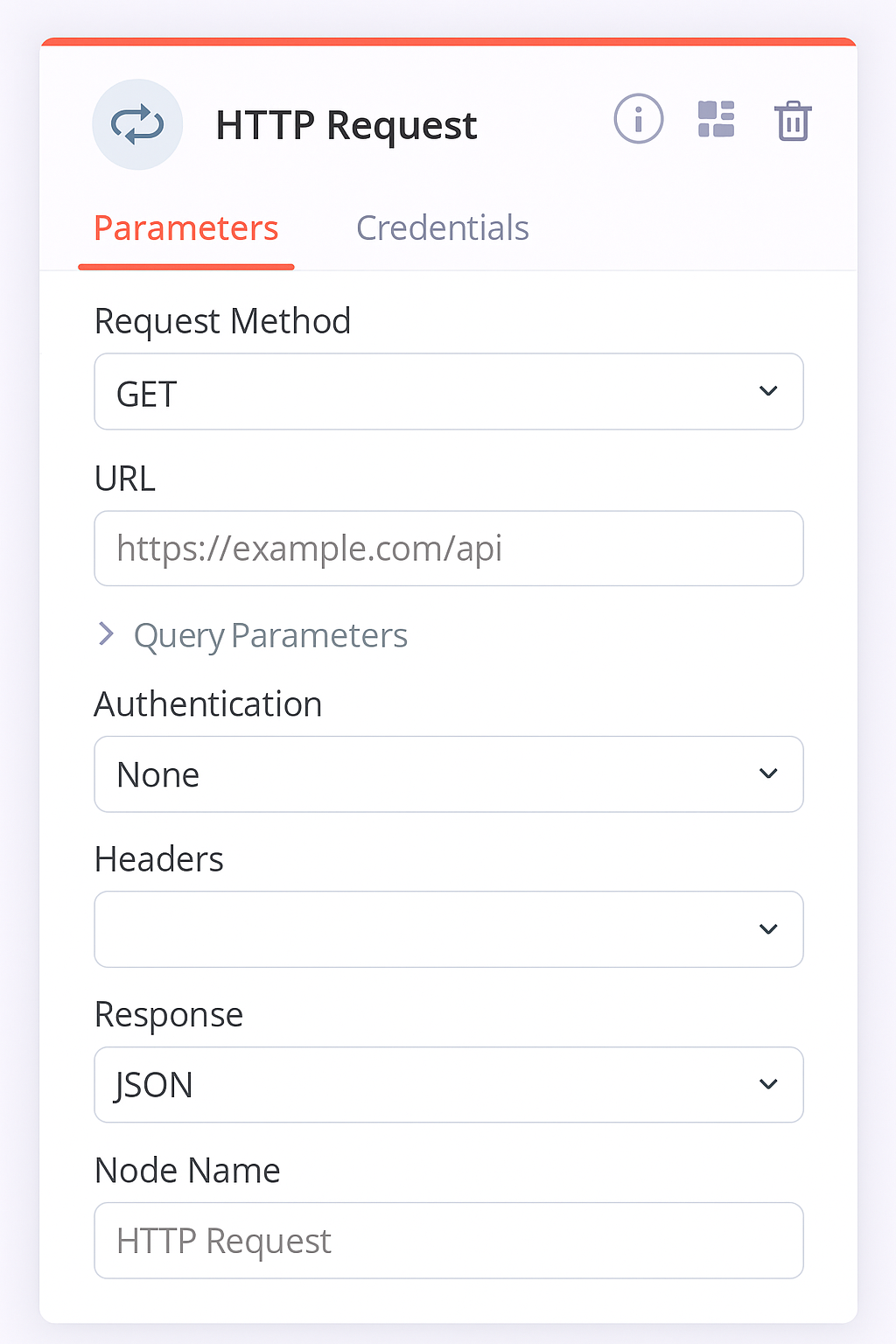
Key Parameters Explained
1. HTTP Method
- GET → Retrieve data
- POST → Send data
- PUT/PATCH → Update data
- DELETE → Remove data
Example:
GET https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts2. URL
Enter the API endpoint you want to call. Example:
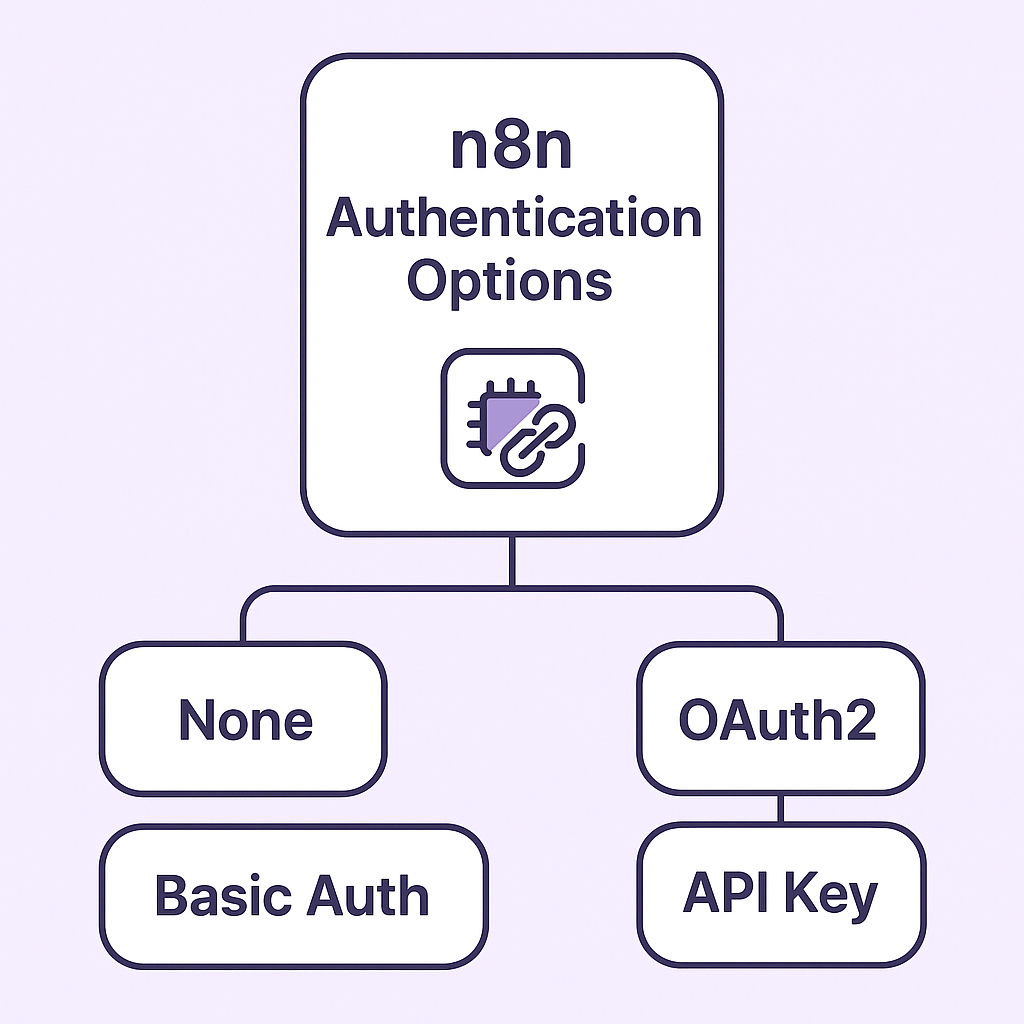
https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions3. Authentication
- None: For public APIs.
- Basic Auth: Username + password.
- OAuth2: Common for Google APIs.
- Header Auth: Add
Authorization: Bearer <token>.
4. Headers
Used to send metadata.
Example for OpenAI:
Authorization: Bearer <API_KEY>
Content-Type: application/json5. Query Parameters
Append key/value pairs to URL. Example:
https://api.example.com/users?role=admin6. Body Content
Choose:
- JSON → Structured data
- Form Data → File uploads
- Raw → Custom payloads
Example JSON body:
{
"name": "Sharad",
"role": "editor"
}Example 1 — GET Request
Fetch posts from JSONPlaceholder:
- Method: GET
- URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts - Auth: None
Response:
[
{ "userId": 1, "id": 1, "title": "Sample post" }
]Example 2 — POST Request with Headers
Send data to an API:
- Method: POST
- URL:
https://api.novamindlabs.com/data - Headers:
Authorization: Bearer <token>Content-Type: application/json
- Body:
{ "task": "Generate blog ideas", "priority": "high" }Common Errors & Fixes
- 401 Unauthorized: Check token/auth.
- 400 Bad Request: Review body format (JSON vs Form).
- 429 Too Many Requests: Add a Wait Node for rate-limiting.
- Timeouts: Increase request timeout in advanced options.
Pro Tips for Using HTTP Request Node
- Test in Postman first → then move into n8n.
- Use Expressions → Example:
{{$json["email"]}}to pass dynamic values. - Set Node Options → Retry on Fail for unstable APIs.
- Combine with Function Node → Transform API responses.
The n8n HTTP Request Node is like a universal remote for APIs—you can call anything, as long as it has an endpoint.
👉 Want to skip trial and error? Novamind Labs is building pre-configured AI + API agents that drop into your workflows.
👉 Or, join my next teaching webinar where I’ll demo real use cases with HTTP Request nodes.
